文章简介:学Java Collections集合,对其中一些知识进行整理
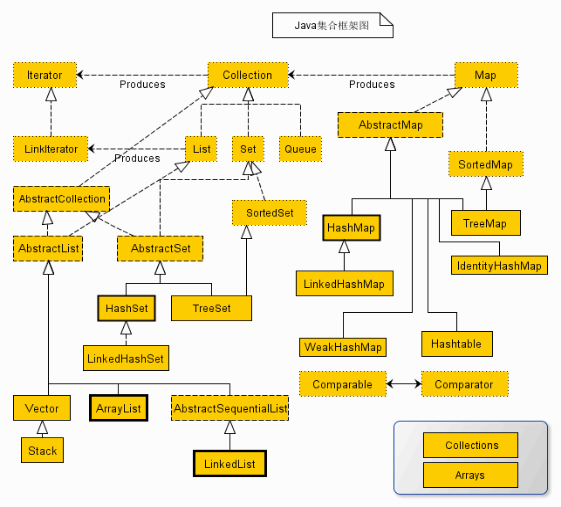
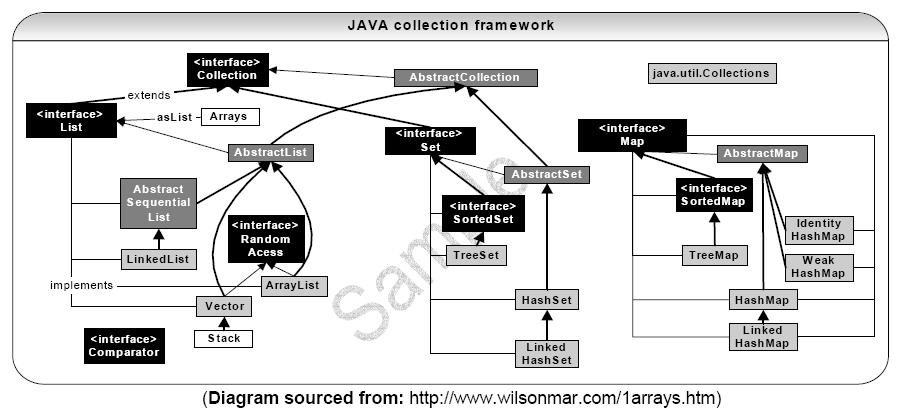
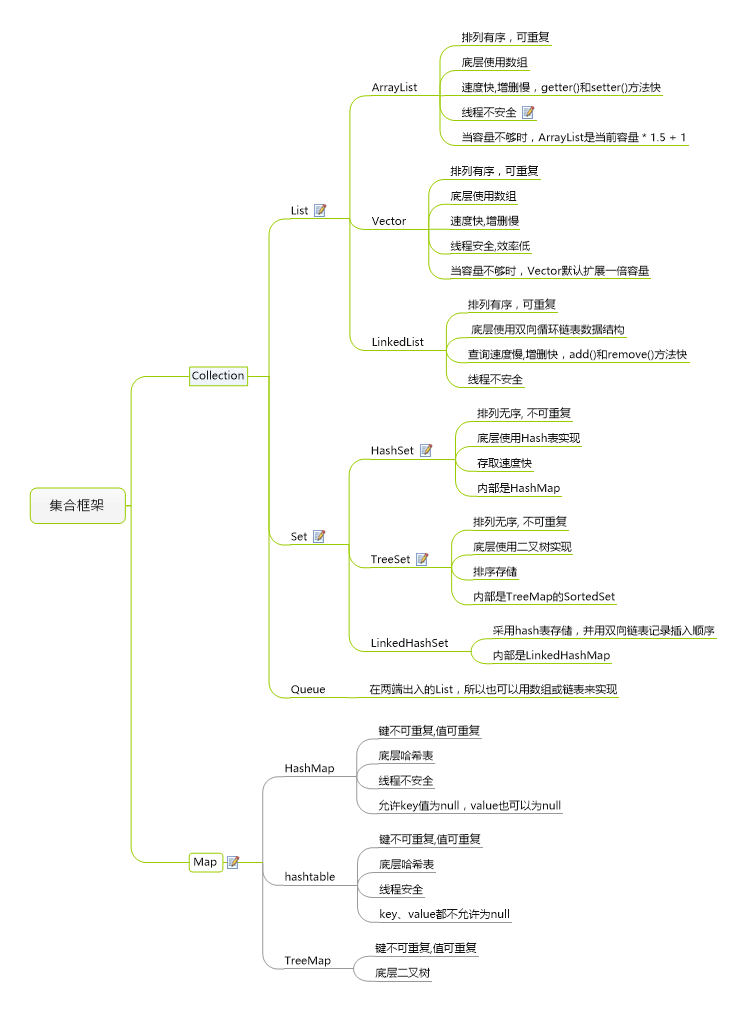
Collections结构



使用例子
Iterator
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public void testIterator(){
//创建一个集合
Collection books = new HashSet();
books.add("轻量级J2EE企业应用实战");
books.add("Struts2权威指南");
books.add("基于J2EE的Ajax宝典");
//获取books集合对应的迭代器
Iterator<String> it = books.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String book = it.next();
System.out.println(book);
if (book.equals("Struts2权威指南")) {
it.remove();
//使用Iterator迭代过程中,不可修改集合元素,下面代码引发异常
//books.remove(book);
}
//对book变量赋值,不会改变集合元素本身
book = "测试字符串";
}
System.out.println(books);
}
|
List
实现List接口的常用类有LinkedList,ArrayList
1
|
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
|
Set
Set接口有以下几种实现:
- HashSet : 为快速查找设计的Set,主要的特点是:不能存放重复元素,而且采用散列的存储方法,所以没有顺序。这里所说的没有顺序是指元素插入的顺序与输出的顺序不一致。
- TreeSet : 保存次序的Set, 底层为树结构。使用它可以从Set中提取有序的序列。
- LinkedHashSet : 具有HashSet的查询速度,且内部使用链表维护元素的顺序(插入的次序)。于是在使用迭代器遍历Set时,结果会按元素插入的次序显示。
1
|
Set<String> hs = new HashSet<>();
|
Map
Map接口有以下几种实现:
HashMap、LinkedHashMap、HashTable和TreeMap
1
2
3
4
|
Map<String, String> m1 = new HashMap<>();
m1.put("Zara", "8");
m1.get("Zara"); // 8
m1.containsKey("Zara"); // true
|
Queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<String>();
//添加元素
queue.offer("a");
queue.offer("b");
queue.offer("c");
queue.offer("d");
queue.offer("e");
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("poll="+queue.poll()); //返回第一个元素,并在队列中删除
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("element="+queue.element()); //返回第一个元素
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
System.out.println("===");
System.out.println("peek="+queue.peek()); //返回第一个元素
for(String q : queue){
System.out.println(q);
}
/*
a b c d e
===
poll=a
b c d e
===
element=b
b c d e
===
peek=b
b c d e
*/
|
转成线程安全
1
|
List<String> list = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList<>());
|
资源